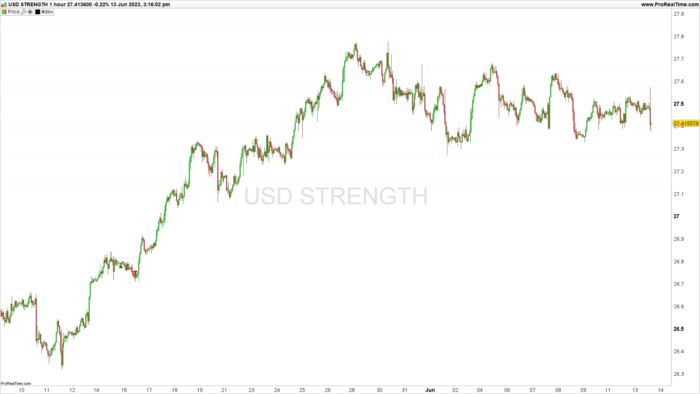
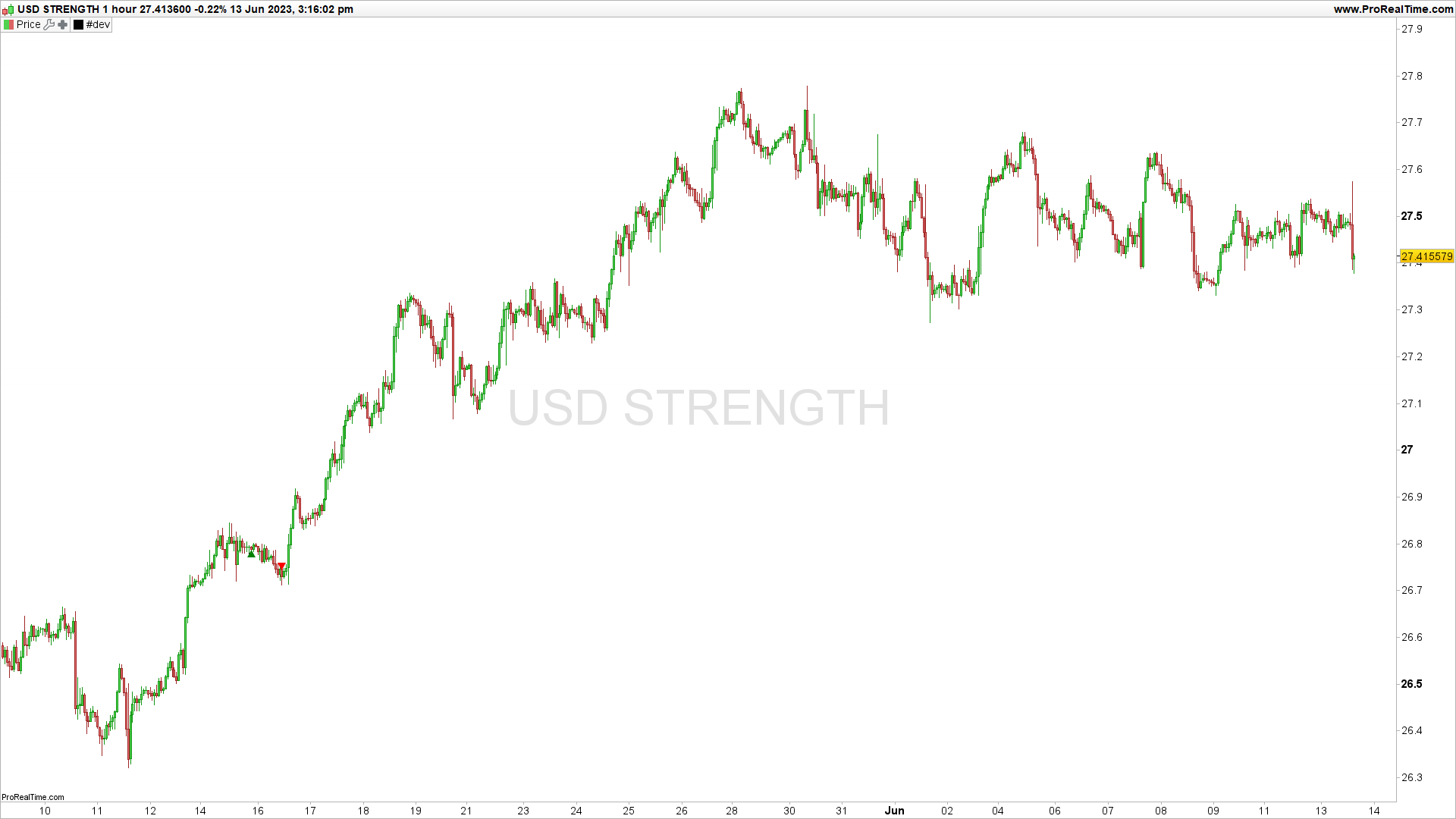
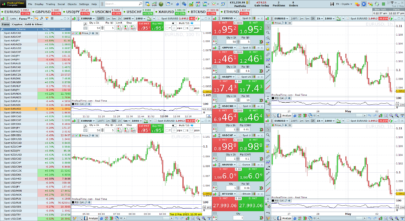
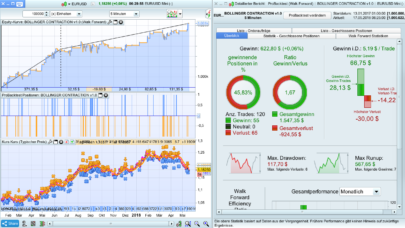
This formula is taking the negative of three currency pairs: GBP/USD, AUD/USD, EUR/USD and adding them to two other currency pairs: USD/JPY, USD/CHF. The result is then divided by 5 to find the average. This could be used as a strategy to determine a portfolio’s average value in currency trading.
Each currency pair represents the cost of one unit of the base currency in terms of the quote currency. For example, if GBP/USD is 1.3, it means 1 British pound is equivalent to 1.3 US dollars.
In this formula, the negative sign before GBP/USD, AUD/USD, and EUR/USD suggests a short position or selling of the base currency (i.e., GBP, AUD, EUR) for US dollars. For USD/JPY and USD/CHF, it implies a long position or buying of US dollars by selling Japanese Yen and Swiss Francs respectively.
Here’s a breakdown:
- -GBP/USD: This signifies a short position on the British pound relative to the US dollar.
- -AUD/USD: This indicates a short position on the Australian dollar relative to the US dollar.
- -EUR/USD: This points to a short position on the euro relative to the US dollar.
- USD/JPY: This signifies a long position on the US dollar relative to the Japanese yen.
- USD/CHF: This indicates a long position on the US dollar relative to the Swiss franc.
By adding these positions together and dividing by 5, the formula is finding the average of these five positions. This could be part of a broader trading strategy in the forex market. The average might be used as a benchmark or as a method to manage risk by diversifying across multiple currency pairs.
Share this
No information on this site is investment advice or a solicitation to buy or sell any financial instrument. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Trading may expose you to risk of loss greater than your deposits and is only suitable for experienced investors who have sufficient financial means to bear such risk.
ProRealTime ITF files and other attachments :PRC is also on YouTube, subscribe to our channel for exclusive content and tutorials